Understanding the Different Types of Electric Engine Options
The future of Volvo vehicles is evolving steadily and upcoming vehicle manufacturing is shifting towards electric vehicles, known as EVs. Not all Electric Vehicles currently on the road and arriving at dealerships are fully 100% operated on electricity; many of them have engines and drivetrains that are known as hybrid or plug-in hybrid.
You must be wondering what are hybrid vehicles or plug-in hybrid vehicles and how are they different from fully electric vehicles? Well, we will find out below the different types of electric vehicles available in the market.
- Battery Operated Electric Vehicle (BEV) or more commonly known simply as EV
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV)
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
- Range Extension Electric Vehicle (REx)
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEVs)
When it comes to the current and near future state of Volvo models, the majority of them will be available as a PHEV or 100% electric EV. Today these options are already available on many of the SUV, sedan and wagons in the lineup. However, the T5 and T6 are still readily available as well. You can learn more about the Volvo T5 and T6 non-electric engines here.
An easy way to understand the difference between the Volvo T8 and P8 engine options is this. The "T" in T8 stands for "Twin Engine", which is Volvo's term for their PHEV models. These are the models that can be plugged in to charge and driven around town using only it's battery technology but can switch to a traditional combustion engine when driving at highway speeds. The "P" in P8 can be thought to stand for "Pure Electric". Volvo models with the P8 engine are fully 100% electric and don't have a secondary traditional gas combustion module. Models with the P8 engine are complete emission free and very quite on both city streets and the highway. Today the only model with a P8 engine option in the U.S. is the XC40, but this option will be coming soon to other models in the lineup. Both the P8 and T8 are AWD.
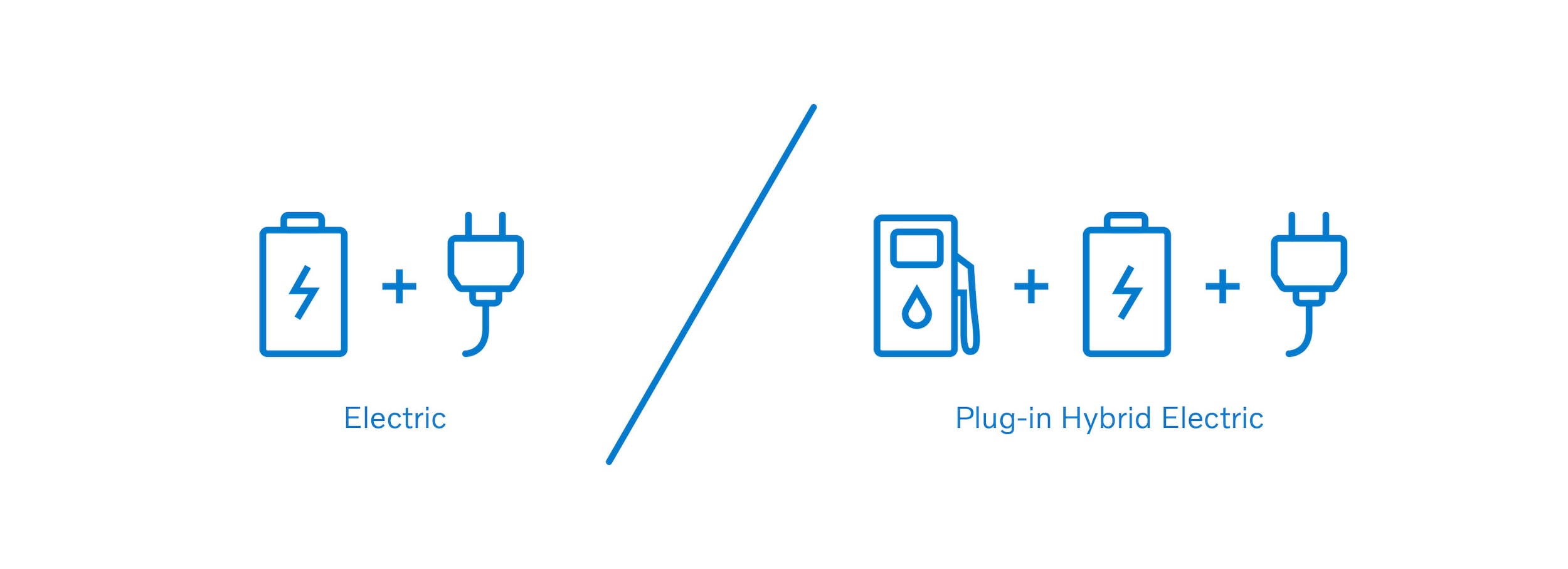
BEV / EV - Battery Operated Electric Vehicle
As the name suggests these vehicles are fully operated through power generated from a battery (Li-ion). This type of vehicle does not come with the traditional combustion engine and because of that emits zero carbon monoxide or pollutants in the atmosphere. A unique feature of BEV/EV models is that they don't have a tailpipe since it is zero emission. In the Volvo line up this would be vehicles with the P8 engine option, which currently includes the XC40 Recharge.
The upcoming all-electric Volvo C40 Recharge is also a BEV/EV and it simply uses the "Recharge Twin" badge foregoing the P8 signifier even though, like the XC40 P8, it is fully electric. This is likely because the C40 is the first Volvo to be built from the ground up as a fully electric vehicle and doesn't have alternate engine option, unlike the XC40 which has both a gas or "ICE" (Internal Combustion Engine) option and a fully electric option, requiring the use of the T and P engine signifiers.
HEV - Hybrid Electric Vehicle
PHEV - Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle
Benefits of PHEVs are the ability to cover shorter distances without using the combustion engine at all and benefit increased range from fuel, battery charging & regenerative braking. In the Volvo lineup this would be any model with the T8 engine option like the XC60 and XC90 today.
REx - Range Extension Types of Electric Vehicles
FCEVs - Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles
Like the BEVs, it does not contain a tailpipe and the byproduct is only water. There is no need to plug-in as the fuel cells are recharged by refilling the hydrogen.